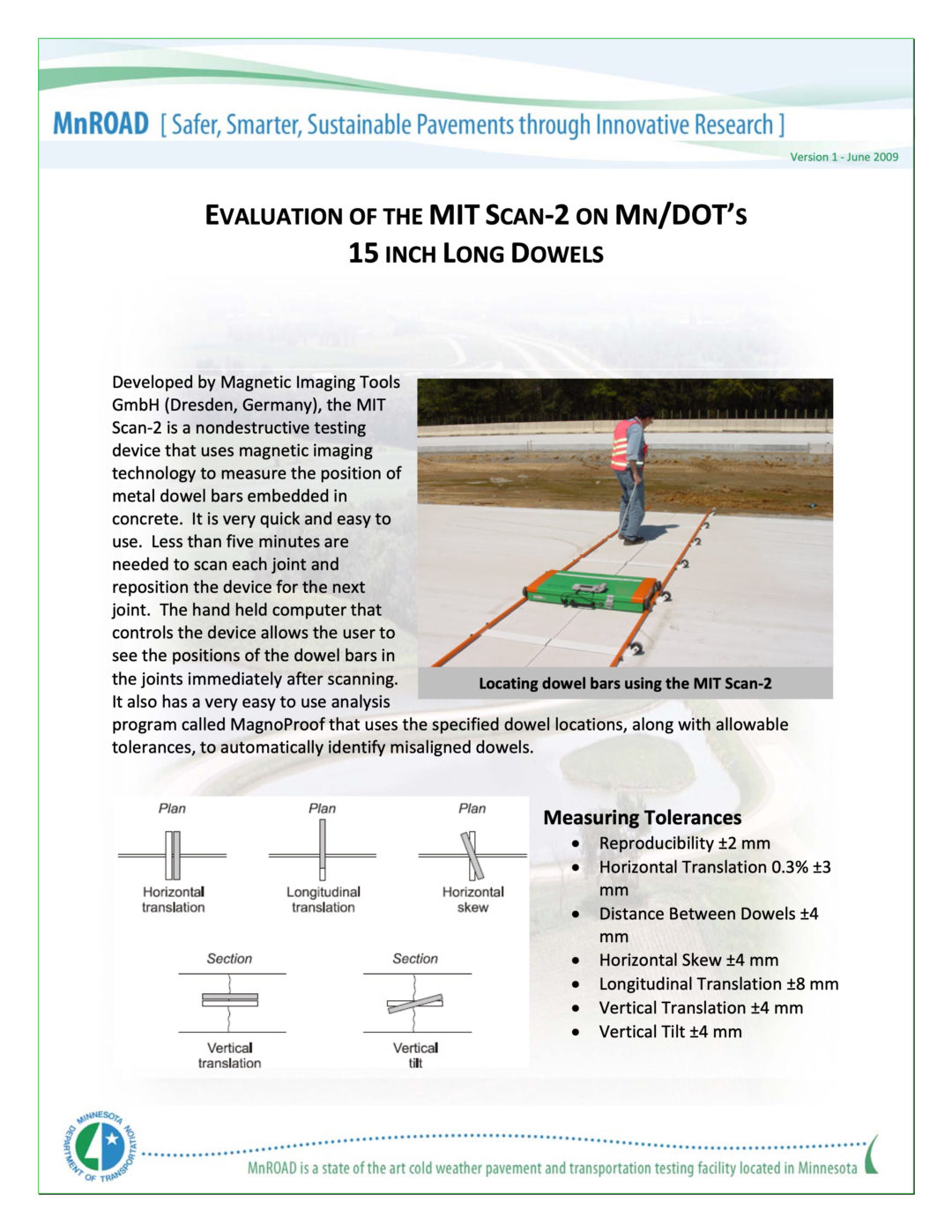
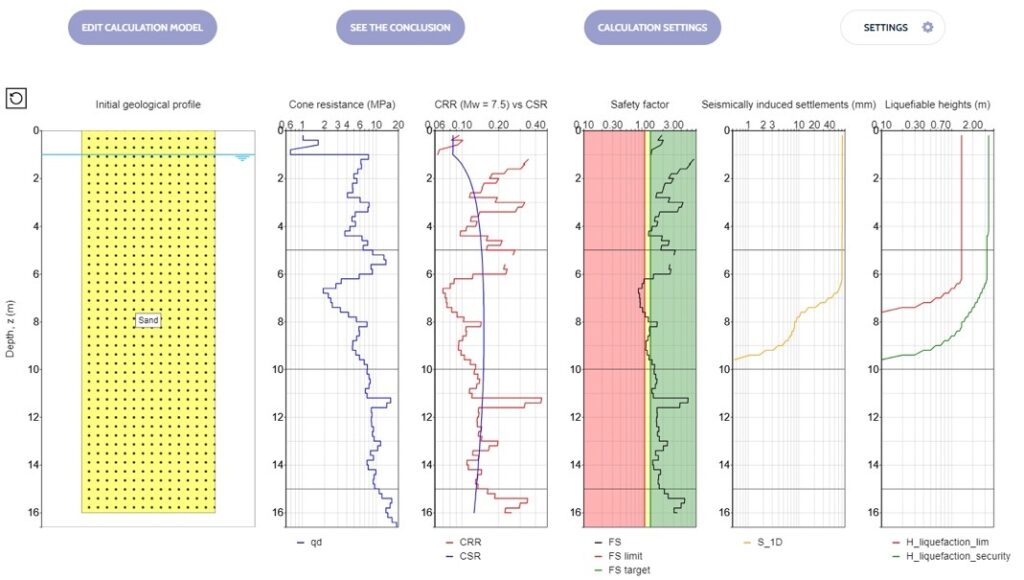
- Non-destructive
- Accurate measurement of dowel bar or tie bar positions and alignment for concrete pavements
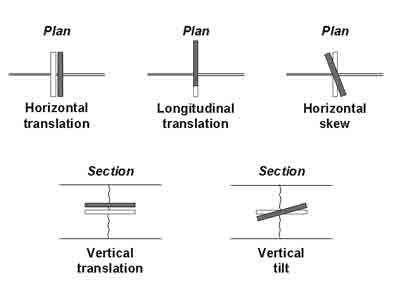
- Horizontal and vertical misalignments with accuracy of ±4 mm and side shifts with accuracy of ± 8 mm
- Meets ASTM E3013 standard
The MIT-DOWEL-SCAN enables the accurate measurement of tie bar / dowel bar position and alignment in concrete pavements.
The equipment is designed with the accuracy required for dowel bars but most clients use it for both dowel bars and tie bars.

Advantages
The advantages include:
- Positioning and alignment can be checked as soon as a person can walk on it after concrete placement
- As the results are immediately available, it allows the contractor to take corrective action immediately, making adjustments during the paving process
- Non-destructive test (NDT) – no need to do coring to measure depth
- One person operation
- Measurement can be taken extremely quickly (less than one minute per joint across several lanes)
- Results are immediately seen on a graphical display on the screen for quality control purposes
- Embedment depths, misalignments & translations are determined precisely, even on rain-drenched surfaces
- Under normal conditions, depths as well as horizontal and vertical misalignments can be determined with an accuracy of ±4 mm and side shifts with an accuracy of ± 8 mm
- Used to evaluate new and existing joints.
- Basket joints can be evaluated if the shipping wires are cut.
The MIT-DOWEL-SCAN from MIT Mess- und Prüftechnik GmbH adheres to ASTM E3013 and is delivered as a complete system ready to use. The measuring vehicle is equipped with an operating unit, a laser unit, MagnoProof software package, manuals and a solid transportation case.
Applications
Concrete pavement applications include:
- Quality Control by contractors for checking their installation process
- Highway construction of plain concrete pavements
- Quality Assurance by owners for accepting completed facilities
- Plain concrete runways, taxiways & ramps at airports
- Concrete Sea Container storage & staging areas in port facilities
- Forensic investigations of failing joints in existing concrete pavements
Why is Alignment and Positioning Important?
Dowel Bars
Properly aligned and embedded dowel bars are vital in jointed plain concrete pavements. Dowel bars are round, smooth, epoxy coated steel bars placed mid‐depth across transverse joints. They allow load transfer whilst allowing the joint to open and they reduce or eliminate faulting and corner cracks. Significantly misaligned dowel bars may lead to joint locking which can cause slabs to crack. Improper placement (embedment) of dowel bars leads to decrease in load transfer efficiency, which can result in faulting and other pavement distresses.
Tie Bars
Tie bars are deformed, epoxy coated steel bars, typically placed mid‐depth across longitudinal joints or between an edge joint and a curb or shoulder. They are designed to prevent lane separation and differential deflection and reduces transverse cracks by holding the faces of abutting slabs in contact. Although they may provide some minimal amount of load transfer, they are not designed to act as load transfer devices and should not be used as such.
Joints
Joints in concrete pavements of highways, airport runways and container areas are exposed to stresses and strains due to traffic and temperature variation. Steel dowel bars, reinforcement bars and tie bars are built into joints, to support the transfer of loads across the joints and to maintain the elevation of adjacent slabs at the joints. The MIT-DOWEL-SCAN is used to determine the number of dowels and tie bars as well as their accurate positions and tolerable displacements, to ensure the long-term performance of the joints.
MIT-DOWEL-SCAN Calibration, Service and Spare Parts
Insitutek are proud to represent MIT Mess- und Prüftechnik MIT-DOWEL-SCAN in Australia, New Zealand and the Pacific Islands and provide a high level of client support.
We offer a complete spectrum of services including after-sale technical support, servicing, repairs, and calibrations.
To find out more, Contact Us.

 The operating principle behind the MIT-DOWEL-SCAN is pulse-induction. The pulse induction method utilizes the magnetic properties of tie bars to create a magnetic field and is referred to as Magnetic Imaging Tomography (MIT). The equipment emits a weak, pulsating, magnetic signal and detects the transient magnetic response signal induced in the metal bars. The response signals are measured with high precision using special receivers in the testing device, permitting the determination of horizontal misalignment, vertical misalignment, side shift and depth of the dowel bar from the top of the pavement.
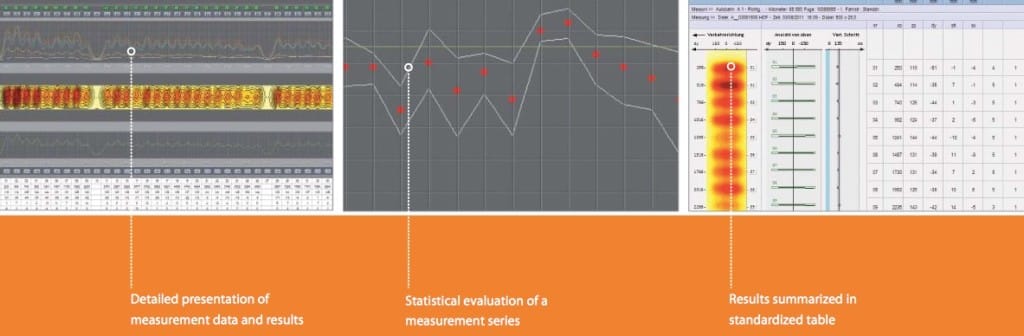
The operating principle behind the MIT-DOWEL-SCAN is pulse-induction. The pulse induction method utilizes the magnetic properties of tie bars to create a magnetic field and is referred to as Magnetic Imaging Tomography (MIT). The equipment emits a weak, pulsating, magnetic signal and detects the transient magnetic response signal induced in the metal bars. The response signals are measured with high precision using special receivers in the testing device, permitting the determination of horizontal misalignment, vertical misalignment, side shift and depth of the dowel bar from the top of the pavement. The MIT-DOWEL-SCAN has 10 sensors and a laser to guide the unit along the joint with great accuracy & repeatability. Results are available directly after the measurement on the screen of the device. Data is visualized as a measuring curve and a colorful map in addition to bar positions and misalignment parameters that are computed. A more detailed analysis of the data can be done by the software MagnoProof on a laptop.
The MIT-DOWEL-SCAN has 10 sensors and a laser to guide the unit along the joint with great accuracy & repeatability. Results are available directly after the measurement on the screen of the device. Data is visualized as a measuring curve and a colorful map in addition to bar positions and misalignment parameters that are computed. A more detailed analysis of the data can be done by the software MagnoProof on a laptop.